 c. α-Carbon
c. α-Carbon Halogenation of the α-carbon
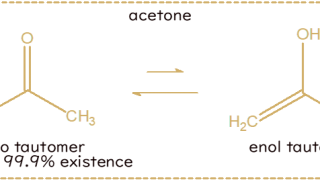
Keto-enol Tautomerismα-hydrogen acidityThe α-hydrogen of a ketone or an aldehyde is more acidic than the α-hydrogen of a...
 c. α-Carbon
c. α-Carbon 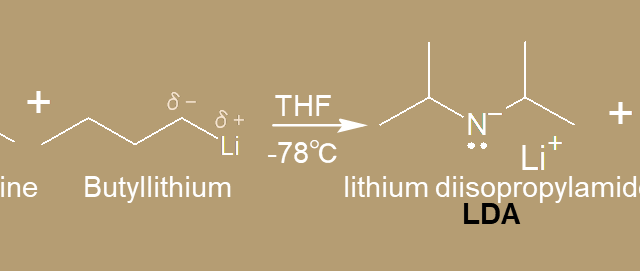 c. α-Carbon
c. α-Carbon  a. Alkenes
a. Alkenes 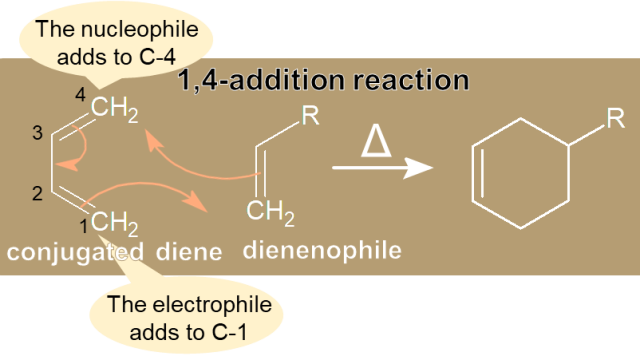 a. Alkenes
a. Alkenes 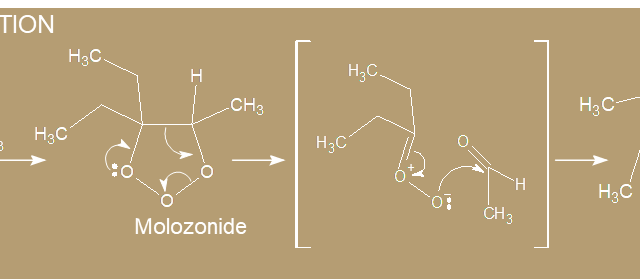 a. Alkenes
a. Alkenes 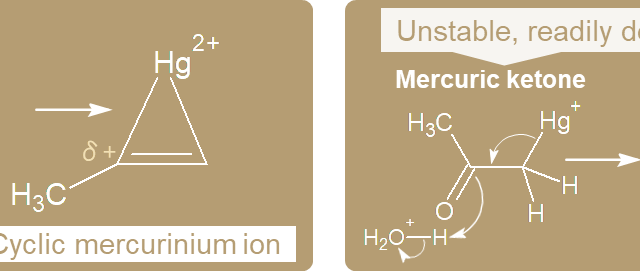 b. Alkynes
b. Alkynes 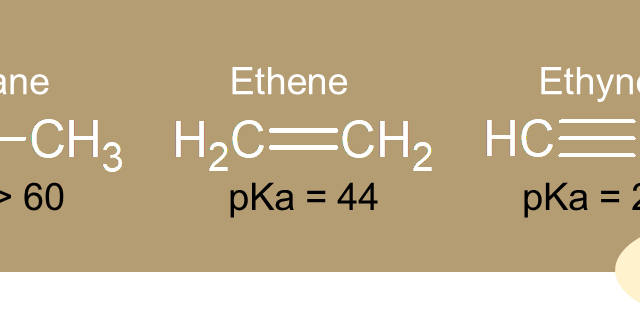 b. Alkynes
b. Alkynes 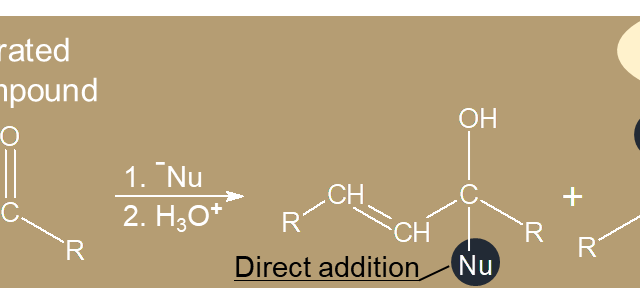 c. α-Carbon
c. α-Carbon 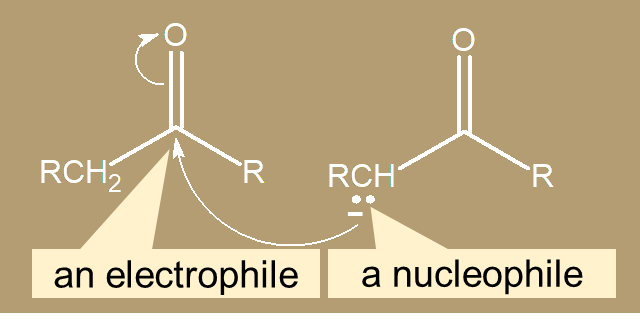 c. α-Carbon
c. α-Carbon 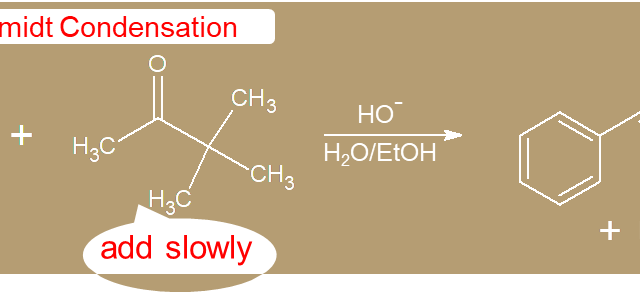 c. α-Carbon
c. α-Carbon  a. Alkenes
a. Alkenes  a. Alkenes
a. Alkenes  a. Alkenes
a. Alkenes  b. Alkynes
b. Alkynes  b. Alkynes
b. Alkynes  c. α-Carbon
c. α-Carbon  c. α-Carbon
c. α-Carbon  c. α-Carbon
c. α-Carbon  c. α-Carbon
c. α-Carbon  c. α-Carbon
c. α-Carbon